Generate prediction points
Insang Song
Source:vignettes/prediction_points.Rmd
prediction_points.RmdObjective
This vignette will demonstrate how the prediction grid points at 1-km
resolution are generated from the polygon data of the mainland US with
terra package.
Strategy
- We set the upper left and lower right corners then make regular grid points at 1,000 meter interval.
-
EPSG:5070, Conus Albers equal area projection, is used throughout this vignette.
usmain <- tigris::states(progress_bar = FALSE)
exclude <- c("02", "15", "60", "66", "68", "69", "72", "78")
usmain <- usmain[!usmain$STATEFP %in% exclude, ]
usmain <- terra::vect(usmain)
usmain <- terra::aggregate(usmain)
usmain <- terra::project(usmain, "EPSG:5070")
plot(usmain)
Generate
Regular or random points can be generated from an extent or a polygon
object with terra::spatSample() or
sf::st_sample(). A faster way of generating regular points
is to leverage a raster object, where cells are organized in a regular
grid. The code block below generates 1-km resolution grid points
following steps:
- Identify corners to generate a rectangular extent (i.e.,
SpatExtentobject fromterra::ext()) - Create a
SpatRasterobject with a fixed resolution and coordinate system (in this case,EPSG:5070) - Assign a value to the void raster
- Crop the raster object with the mainland US polygon
- Convert the cropped raster to points (we have a
SpatVectorobject) - Convert the
SpatVectorobject to a three-columndata.frameobject - Save the
data.frameobject from step 6 as an RDS file
Steps 6 and 7 reduce the file size substantially as all data in the
data.frame from step 6 are in numeric type. This means the
data can be compressed efficiently.
corner_ul <- c(-2.40, 3.26) * 1e6
corner_lr <- c(2.40, 0.12) * 1e6
corners <- c(corner_ul, corner_lr)
# reorganize xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, which are ll, ur form
corners_re <- corners[c(1, 3, 4, 2)]
names(corners_re) <- c("xmin", "xmax", "ymin", "ymax")
corners_ext <- terra::ext(corners_re)
corners_ras <-
terra::rast(
corners_ext,
resolution = c(1000L, 1000L),
crs = "EPSG:5070"
)
terra::values(corners_ras) <- 1L
corners_ras_sub <-
terra::crop(
corners_ras,
usmain,
snap = "out",
mask = TRUE
)
corners_pnts <- terra::as.points(corners_ras_sub)
corners_pnts_df <- as.data.frame(corners_pnts, geom = "XY")
corners_pnts_df$site_id <- seq(1, nrow(corners_pnts_df))
names(corners_pnts_df)[2:3] <- c("lon", "lat")
corners_pnts_df <- corners_pnts_df[, c("site_id", "lon", "lat")]
saveRDS(
corners_pnts_df,
file = "./input/prediction_grid.rds",
compress = "xz"
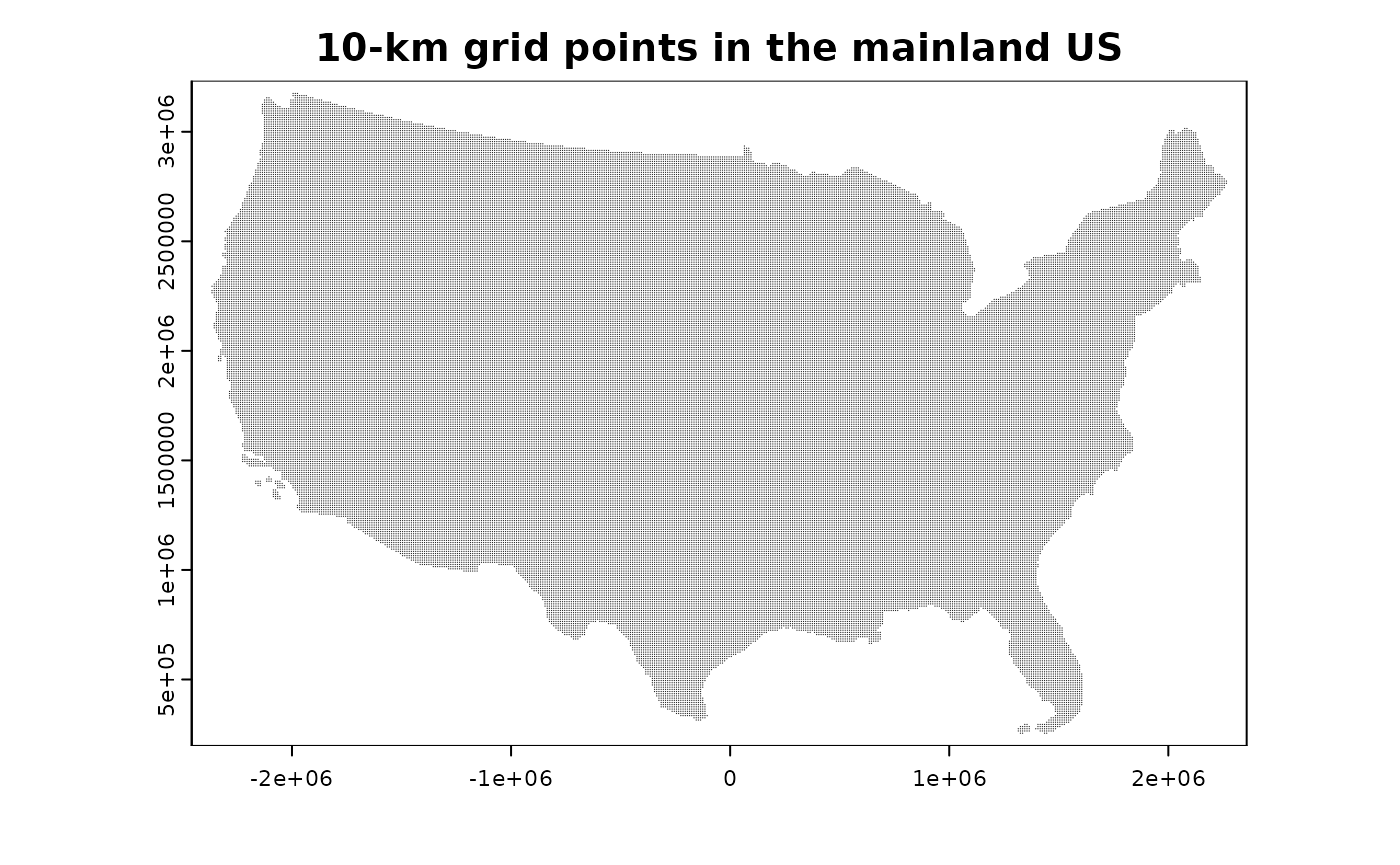
)Below is a map of 10-km grid points in the mainland US for faster rendering. The actual 1-km result will look denser.
plot(
corners_pnts10,
cex = 0.1,
main = "10-km grid points in the mainland US"
)