NOAA North American Regional Reanalysis (NARR)
Mitchell Manware
2026-01-27
Source:vignettes/narr_workflow.Rmd
narr_workflow.RmdThis vignette demonstrates how to download, process, and calculate
covariates from the NOAA North
American Regional Reanalysis (NARR) dataset using
amadeus functions. Details are provided for each function’s
parameters and outputs. The examples utilize daily air temperature at 2m
height (“air.2m”) data. The messages returned by amadeus
functions have been omitted for brevity.
Download
Start by downloading the netCDF data files with
download_data.
-
dataset_name = "narr": NARR dataset acronym. -
variable = "air.2m": air temperature at 2m height variable code. -
year = c(2021, 2022): years of interest. -
directory_to_save = dir: directory to save the downloaded files. -
acknowledgement = TRUE: acknowledge that the raw data files are large and may consume lots of local storage. -
download = TRUE: download the data files. -
remove_command = TRUE: remove the temporary command file used to download the data. -
hash = TRUE: generate unique SHA-1 hash for the downloaded files.
dir <- tempdir()
amadeus::download_data(
dataset_name = "narr",
variable = "air.2m",
year = c(2021, 2022),
directory_to_save = dir,
acknowledgement = TRUE,
download = TRUE,
remove_command = TRUE,
hash = TRUE
)[1] "3a382ac1c383c1d048f4044214cb450f"Check the downloaded netCDF files.
list.files(dir, recursive = TRUE, pattern = "air.2m")[1] "air.2m/air.2m.2021.nc" "air.2m/air.2m.2022.nc"Process
Import and process the downloaded netCDF files with
process_covariates.
-
covariate = "narr": NARR dataset acronym. -
variable = "air.2m": air temperature at 2m height variable code. -
date = c("2021-12-28", "2022-01-03"): date range of interest. -
path = paste0(dir, "/air.2m"): directory containing the downloaded files.
air2m_process <- amadeus::process_covariates(
covariate = "narr",
variable = "air.2m",
date = c("2021-12-28", "2022-01-03"),
path = file.path(dir, "/air.2m")
)Check the processed SpatRaster object.
air2m_processclass : SpatRaster
dimensions : 277, 349, 7 (nrow, ncol, nlyr)
resolution : 32462.99, 32463 (x, y)
extent : -16231.49, 11313351, -16231.5, 8976020 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
coord. ref. : +proj=lcc +lat_0=50 +lon_0=-107 +lat_1=50 +lat_2=50 +x_0=5632642.22547 +y_0=4612545.65137 +datum=WGS84 +units=m +no_defs
sources : air.2m.2021.nc:air (4 layers)
air.2m.2022.nc:air (3 layers)
varnames : air (Daily Air Temperature at 2 m)
air (Daily Air Temperature at 2 m)
names : air.2~11228, air.2~11229, air.2~11230, air.2~11231, air.2~20101, air.2~20102, ...
unit : K, K, K, K, K, K, ...
time : 2021-12-28 to 2022-01-03 UTC
terra::plot(air2m_process[[1]])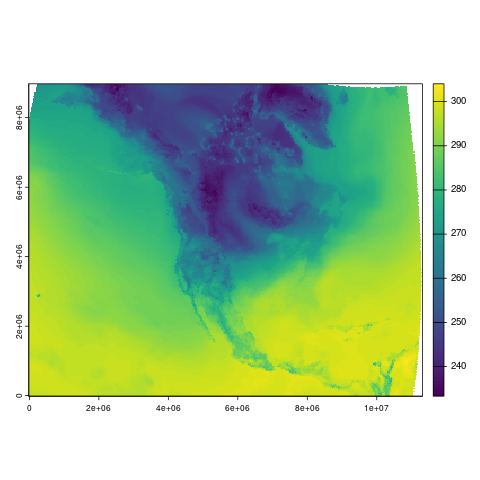
Calculate covariates
Calculate covariates for North Carolina county boundaries with
calculate_covariates. County boundaries are accessed with
the tigris::counties function.
-
covariate = "narr": NARR dataset acronym. -
from = air2m_process: processedSpatRasterobject. -
locs = tigris::counties("NC", year = 2021): North Carolina county boundaries. -
locs_id = "NAME": county name identifier. -
radius = 0: size of buffer radius around each county. -
geom = "terra": return covariates as aSpatVectorobject.
library(tigris)
air2m_covar <- amadeus::calculate_covariates(
covariate = "narr",
from = air2m_process,
locs = tigris::counties("NC", year = 2021),
locs_id = "NAME",
radius = 0,
geom = "terra"
)Check the calculated covariates SpatVector object.
air2m_covarclass : SpatVector
geometry : polygons
dimensions : 700, 3 (geometries, attributes)
extent : 7731783, 8506154, 3248490, 3694532 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
coord. ref. : +proj=lcc +lat_0=50 +lon_0=-107 +lat_1=50 +lat_2=50 +x_0=5632642.22547 +y_0=4612545.65137 +datum=WGS84 +units=m +no_defs
names : NAME time air.2m_0
type : <chr> <POSIXt> <num>
values : Chatham 2021-12-28 289.3
Alamance 2021-12-28 288.8
Davidson 2021-12-28 289.1Temporal summaries
The aggregate function can be used to calculate a
summary statistic for each unique spatial point or polygon. In the
following example, average air.2m_0 is calculated for each
county for the time period December 28, 2021 to January 3, 2022.
air.2m_0 ~ NAME directs the function to summarize
air.2m_0 values per unique NAME. The
FUN = mean directs the function to take the mean value. The
head() function is applied to show only the first few
entries, as the entire data.frame is 100 rows long.
NAME air.2m_0
1 Alamance 289.5930
2 Alexander 289.1961
3 Alleghany 286.9486
4 Anson 290.5306
5 Ashe 285.5771
6 Avery 285.2288